Effective Hair Loss Treatments for Men: Stop Balding & Regrow Hair
Understanding Hair Loss In Men
A In recent years, men have been experiencing balding at increasingly younger ages. Many men, particularly those in their 20s and 30s, are facing hair loss earlier than in previous generations. This has had a significant impact on their self-esteem and mental well-being.
The leading cause of male hair loss is androgenetic alopecia (AGA), commonly referred to as male pattern baldness (MPB), which is primarily driven by genetics and sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT). It typically starts with a receding hairline or thinning at the crown.
Beyond male pattern baldness, other types of balding, such as telogen effluvium—often triggered by stress, illness, or nutritional deficiencies—and scarring alopecia, which results from inflammation damaging hair follicles, can also contribute to the issue.

What Causes Hair Loss In Men?
Understanding the causes of hair loss in men is the first step in addressing the issue. Here are the main reasons men experience hair thinning or baldness:
- Androgenetic Alopecia (Male Pattern Baldness): A genetic condition caused by the hormone DHT, leading to thinning and eventual baldness.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Fluctuations in hormones like testosterone and thyroid hormones can result in hair loss.
- Telogen Effluvium: Temporary shedding of hair triggered by stress, illness, or significant life changes.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Insufficient levels of iron, zinc, or vitamins such as D can cause thinning or shedding of hair.
- Medications: Certain drugs like chemotherapy agents, blood thinners, and others can lead to hair loss.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like alopecia areata and lupus can cause the immune system to attack hair follicles, leading to thinning.
- Scarring Alopecia (Cicatricial Alopecia): Permanent hair loss caused by inflammation and scarring of the hair follicles.
- Excessive Hair Care Practices: Regular use of tight hairstyles, harsh chemicals, and heat styling can lead to hair damage.
- Lifestyle Factors: Unhealthy habits such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and chronic stress can negatively affect hair health.
Signs of Hair Loss In Men
Some common signs of hair loss in men include:
- Receding Hairline: One of the earliest and most noticeable signs, especially along the temples. This is common in male pattern hair loss and can gradually worsen over time.
- Thinning Crown: Thinning at the top of the head or crown is another early sign of androgenetic alopecia. It often leads to a noticeable bald spot.
- Widening Part: As the hair thins, the parting of the hair may become more noticeable, particularly on the top or sides of the scalp.
- Excessive Shedding: Finding more hair in the shower or on your pillow at night can be a sign that you are losing hair at a faster rate than normal.
- Patchy Hair Loss: In some cases, men may notice small, circular patches of hair thinning, which could be a sign of alopecia areata or other medical conditions.
- Change in Hair Texture: As hair follicles weaken, hair may become finer, thinner, or more brittle, making it prone to breakage.
- Visible Scalp: As hair density decreases, the scalp may become more visible, particularly in areas where hair is thinning.
- Excessive Shedding After Washing: Hair loss that occurs after washing or combing is common as hair weakens and falls out during these activities.
Understanding The Norwood Scale: Classification of Male Pattern Baldness
The Norwood Scale is a widely used tool to classify the stages of male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia), providing insight into both the extent and severity of balding in men. This scale helps doctors and patients track the progression of hair loss over time, from the initial stages of a slight recession to the most advanced form of baldness.
Here’s a breakdown of the Norwood Scale stages:
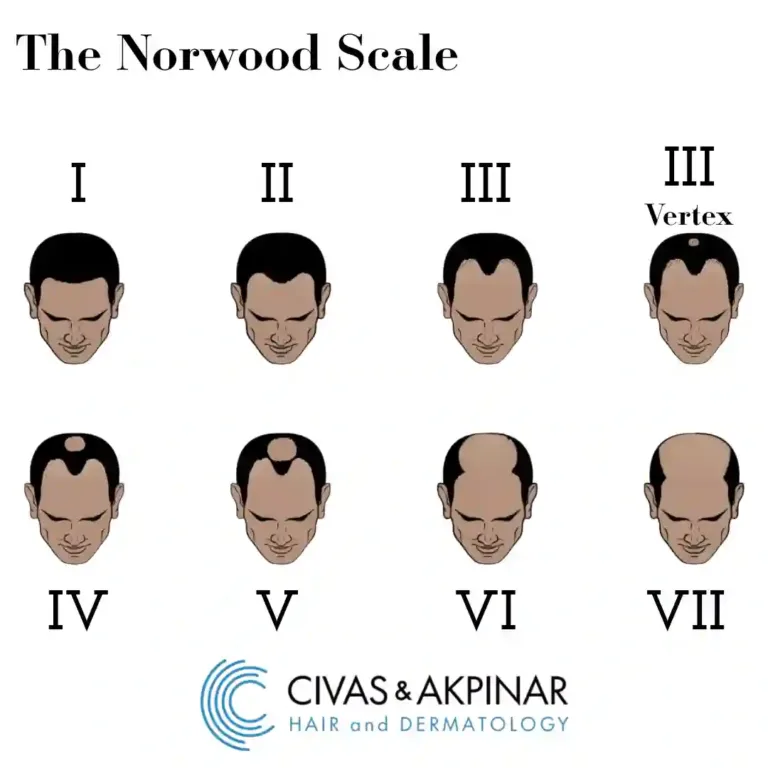
Stage 1: No visible hair loss or recession of the hairline, indicating minimal or no signs of hair thinning.
Stage 2: A mild recession of the hairline at the temples, marking the beginning of noticeable thinning.
Stage 3: Clear thinning at the temples and crown, with more significant signs of hair loss.
Stage 4: Increased recession of the hairline and more pronounced thinning at the crown, indicating moderate to severe hair loss.
Stage 5: A larger bald area on the crown and front of the scalp, with the “U” shape becoming more defined.
Stage 6: Significant baldness, where the front and crown areas merge, leaving only a small band of hair along the sides of the head.
Stage 7: The most severe stage, where hair loss is almost complete, with only a thin band of hair remaining on the sides and back of the head.
How Can You Prevent Hair Loss?
In cases where hair loss can be prevented, adopting certain habits can slow down the process or reduce its severity.
Here are some strategies to consider:
Healthy Diet: A well-balanced diet, rich in vitamins and minerals like vitamin D, iron, zinc, and biotin, can significantly benefit hair health.
Minimize Stress: Reducing stress through activities like meditation, yoga, or regular exercise can help protect against hair loss.
Gentle Hair Care: Avoid over-brushing, excessive use of heat styling tools, or harsh chemical products that can damage hair.
Appropriate Hairstyles: Avoid tight hairstyles to prevent traction alopecia, a type of hair loss caused by tension on hair follicles.
Avoid Smoking: Smoking can restrict blood flow to the scalp, impairing hair follicle health and accelerating hair loss. Studies suggest that people who smoke tend to experience faster hair thinning than non-smokers.
Tricopat Therapy: Tricopat Therapy is another non-surgical treatment that utilizes micro-stimulation and the application of specific scalp solutions to improve hair health.
The earlier you detect hair thinning or a receding hairline, the more effective your treatment options will be.
What Is the Best Hair Loss Treatment For Men?
When it comes to hair loss solutions for men, the options range from non-invasive solutions to surgical interventions, depending on the severity of hair loss and your specific needs. Medications such as Minoxidil, Finasteride, and Dutasteride are widely used to slow baldness and promote regrowth by targeting hair follicle health and hormone regulation. For those seeking long-lasting, permanent results, hair transplant procedures can be considered to restore hair density in balding areas.
Hair Loss Treatments For Men: Pros and Cons
Hair loss in men can be treated using various methods, each with unique benefits and potential drawbacks.
1. Finasteride:
Finasteride blocks the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, reducing DHT (a hormone that shrinks hair follicles) levels in the scalp, slowing hair loss and promoting regrowth.
Pros: Effective in treating male pattern baldness; easy to use as a daily oral medication.
Cons: May cause side effects like decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, or mood changes. Results stop if the medication is discontinued.
2. Dutasteride:
Dutasteride inhibits both Type I and Type II 5-alpha reductase enzymes, making it a stronger DHT blocker than Finasteride.
Pros: More potent for advanced hair loss; can stabilize hair thinning and stimulate regrowth.
Cons: Similar side effects to Finasteride, with potential for stronger hormonal changes. It is not FDA-approved for hair loss in some countries.
3. Minoxidil:
Minoxidil widens blood vessels in the scalp, improving blood flow and nutrient delivery to hair follicles, encouraging regrowth.
Pros: Easily accessible and affordable topical solution; stimulates hair growth and thickening.
Cons: Requires consistent application to maintain results; potential scalp irritation or unwanted facial hair growth. Minoxidil can be toxic to cats if ingested or absorbed through their skin, so it must be applied carefully and kept away from pets.


4. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT):
LLLT uses red light wavelengths to stimulate hair follicles, increase cellular activity, and promote hair regrowth.
Pros: Non-invasive, pain-free treatment; improves hair density when used regularly.
Cons: Effectiveness varies; requires long-term commitment; devices are often costly.
5. Hair Transplant Surgery:
Hair follicles are harvested from the safe donor area and transplanted to balding or thinning areas to achieve permanent hair restoration.
Pros: Offers natural-looking, permanent results; ideal for advanced hair loss.
Cons: Expensive; requires downtime for recovery; risk of scarring if not performed by an experienced hair transplant surgeon.
6. Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP):
SMP is a specialized tattooing technique that deposits pigment into the scalp to mimic the appearance of hair follicles, creating the illusion of a fuller scalp.
Pros: Quick results; cost-effective; requires no downtime.
Cons: Does not regrow hair; semi-permanent and may need touch-ups over time.
7. Stem Cell Therapy:
Stem cells are extracted and injected into the scalp to regenerate and activate dormant hair follicles, promoting natural hair growth.
Pros: Innovative and regenerative treatment; may improve hair density and thickness.
Cons: Still experimental with limited availability; expensive, and results may vary.
How Effective Are Male Hair Loss Treatments?
The effectiveness of malehair loss treatments largely depends on the chosen method, the stage of balding, and factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and overall health.
Non-surgical options like Minoxidil and Finasteride can be highly effective in slowing hair loss and encouraging regrowth, especially when used early.
Hair restoration procedures, such as FUE and DHI, are considered the most effective for achieving permanent, natural-looking results, especially in cases of advanced hair loss.
However, consistency and patience are key, as most treatment modalities require several months to show visible improvements.
When Is A Hair Transplant The Right Option?
A hair transplant is the right option when hair loss has progressed to a point where non-surgical treatments like Minoxidil or Finasteride are no longer effective or in cases where the patient desires a permanent solution.
Ideal candidates for hair transplantation are those with sufficient donor hair in the back or sides of the scalp, as these areas are typically resistant to DHT and hair thinning.
Hair transplants are particularly suitable for patients with androgenetic alopecia (male pattern baldness), as well as those with hair loss due to injury or scarring.
Choosing The Right Hair Loss Treatment For You
Choosing the right hair loss treatment begins with a proper diagnosis to identify the root cause of your hair loss. Factors such as genetics, hormonal imbalances, medical conditions, or lifestyle habits can all contribute to hair thinning or balding, and addressing the underlying issue is key to finding the most effective solution.
Consulting a dermatologist is essential, as they can assess your scalp, perform necessary tests, and recommend a tailored treatment plan.
At Civas&Akpınar Hair Transplant in Turkey, our expert dermatologists have years of experience in diagnosing and treating various types of hair loss. Whether you need medical therapy or a hair transplant, we are here to guide you every step of the way.
Fill out the contact page below, and we’ll get in touch with you to begin your journey to restored confidence.


