Top Hair Loss Treatments for Women: Restore Thinning Hair Naturally
Understanding Hair Loss In Women
Hair is often seen as a symbol of beauty, femininity, and identity for women, making it an integral part of self-expression and confidence. When hair loss occurs, whether due to hormonal imbalances, genetics, or other medical conditions, it can lead to emotional distress and a significant drop in self-esteem.
For many women, thinning hair or bald spots may feel like losing control over their appearance, impacting social interactions and mental well-being. This emotional toll highlights the importance of addressing hair loss not just as a cosmetic issue but as a quality-of-life concern.

Is Female Hair Loss Different From Male Hair Loss?
Female hair loss differs from male hair loss in several ways, both in terms of its causes and patterns. While men often experience male pattern baldness, which typically begins at the hairline and results in noticeable bald patchesor a receding hairline, female patients usually experience more diffuse thinning across the scalp.
Women are less likely to go completely bald, but they may notice a general decrease in volume, particularly at the crown. Androgenetic alopecia, the most common cause of shedding in both men and women, affects women differently; for example, they may experience thinning that starts later in life, often after menopause, due to hormonal changes.
Other factors, such as pregnancy, stress, and autoimmune conditions, can also contribute to hair loss in women, but these are typically less prominent in male-pattern baldness.
What Causes Hair Loss In Women?
Hair loss in women can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Genetic Factors (Androgenetic Alopecia): The most common cause of female hair loss is genetic. Also known as female pattern baldness, AGA leads to diffuse thinning, typically around the crown and parting of the hair.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Hormonal changes due to pregnancy, childbirth, or menopause can significantly impact hair health. Women may experience temporary or permanent thinning after pregnancy (postpartum hair loss) or during menopause due to the decline in estrogen and progesterone levels.
- Thyroid Disorders: Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are common thyroid conditions that can disrupt hair growth. A sluggish thyroid (hypothyroidism) can cause hair to become dry and brittle, leading to thinning or shedding.
- Stress: Physical or emotional stress can trigger a type of shedding called telogen effluvium, where hair prematurely enters the shedding phase. This condition is often temporary, but prolonged stress can have lasting effects on hair health.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Lack of vital nutrients, such as iron, zinc, and biotin, can lead to hair thinning or shedding.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like alopecia areata (an autoimmune disorder), lupus, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can contribute to hair loss.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs, can also cause hair shedding as a side effect.
- Tight Hairstyles and Hair Damage: Traction alopecia can result from hairstyles that pull tightly on the hairstrands, such as braids or ponytails. Overuse of heat styling tools, chemical treatments, or harsh hair products can also weaken hair, causing it to break or fall out.
- Age: As women age, hair growth naturally slows down, and hair may become thinner over time. Age-related hair thinning is typically a gradual process that affects the scalp’s density.
Signs of Hair Loss In Women
Hair loss in women can manifest in various ways, and recognizing the early signs is crucial for effective treatment. Some common signs include:
- Diffused Thinning: One of the most common early signs of hair loss in women is gradual thinning all over the scalp, with the hair seeming less dense.
- Increased Shedding: If you notice more hair on your pillow, in the shower drain, or your brush, it could indicate that you’re shedding more hair than usual. While some shedding is normal, an increase can point to underlying issues.
- Wider Parting: A widening of the part in your hair is often an early sign of thinning. This can become more noticeable over time.
- Receding Hairline: While this is more common in men, some women experience a receding hairline due to hormonal changes or genetics. This can start subtly but may lead to noticeable changes around the temples.
- Brittle or Dry Hair: If your hair starts to feel dry, brittle, or fragile, it may be an indicator of hair loss. Thin, dry strands break easily, leading to a loss of volume.
- Visible Scalp: As hair begins to thin, the scalp may become visible through the hair, particularly in areas like the crown or along the hairline. This is a sign that the hair follicles may not be growing new hair as quickly as before.
- Change in Texture or Growth Patterns: A noticeable change in hair texture, such as finer, softer, or slower-growing strands, can indicate hair loss. If your hair stops growing at its usual rate, it may be a sign of underlying issues.
Understanding The Ludwig Scale: Classification Of Female Pattern Baldness.
This scale helps doctors in assessing the extent of hair thinning in female patients and aids in treatment planning.
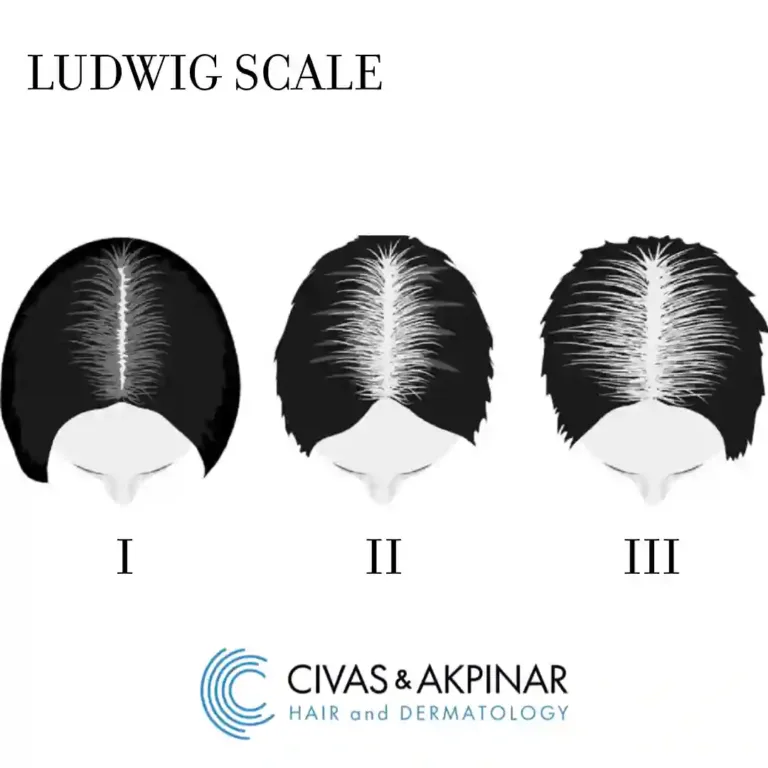
The Ludwig scale has three primary stages:
Stage I: This is the earliest stage of female pattern baldness, characterized by slight thinning of the hair, particularly at the crown or top of the head.
Stage II: At this stage, the scalp becomes more visible through the hair with the crown area losing density. The thinning may start to extend to the frontal area, though the hairline typically remains intact.
Stage III: The crown and other areas of the head have significant hair loss, and the scalp becomes highly visible. In some cases, the thinning may extend to the entire top portion of the scalp, leaving only a thin fringe of hair along the sides.
How Can You Prevent Hair Loss In Women?
Here are some effective ways to help prevent hair loss in female patients:
- Maintain a Balanced Diet: Eating a nutrient-rich diet can support healthy hair growth. Vitamins and minerals such as biotin, iron, zinc, and vitamins A, C, and D play an essential role in hair health.
- Reduce Stress: Managing stress through regular exercise, meditation, and relaxation techniques can reduce its impact on hair health.
- Use Gentle Hair Care Products: Avoid harsh shampoos, conditioners, and styling products that can weaken hair.
- Avoid Tight Hairstyles: Avoiding hairstyles that pull tightly on the hair, such as ponytails, braids, or buns, and allowing your hair to relax can prevent unnecessary stress on the hair follicles.
- Be Gentle When Styling: Brush your hair gently and avoid tugging, especially when it’s wet, as this is when hair is most vulnerable to breakage.
- Address Underlying Health Issues: Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders, PCOS, and autoimmune diseases, can contribute to hair loss. Seeking treatment for these conditions may help prevent further hair thinning.
- Limit Chemical Exposure: Limiting the use of chemical treatments, such as perms, relaxers, or hair dyes, can reduce the risk of hair damage and thinning.
- UV Protection: Wearing a hat or using hair products with SPF can protect your hair from sun damage.
What Are The Best Treatments For Hair Loss In Women?
The best treatment for hair loss in women depends on the underlying cause of the condition and the individual needs of the patient. Treatments like Minoxidil may work well for female patients experiencing hormonal hair loss, while options like hair transplant surgery may be more suitable for those with advanced thinning.
Nutritional supplements or lifestyle changes can be beneficial if deficiencies are contributing to hair loss, and therapies such asLow-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) can promote hair growth in early stages.
Hair Loss Treatments For Women: Pros And Cons
Here are the top treatments for hair loss in women:
1. Minoxidil (Rogaine):
Minoxidil is a topical treatment that stimulates hair follicles to promote hair regrowth. It works by increasing blood flow to the scalp, encouraging new hair growth.
Pros: FDA-approved for female pattern baldness. Non-invasive and easy to use.
Cons: Results can take several months to become noticeable. Must be used indefinitely for continued results. Some users may experience scalp irritation or dryness.
2. Hair Transplant Surgery:
Hair transplant for women involves relocating hair follicles from areas with dense hair to areas experiencing thinning or baldness.
Pros: Provides permanent, natural-looking results when performed by an experienced hair transplant doctor. Can restore significant hair loss in patients with more advanced stages of thinning.
Cons: Expensive and requires a surgical procedure with recovery time. Results may take several months to become fully visible.
3. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT):
LLLT uses laser light to stimulate hair follicles, improve blood circulation to the scalp, and encourage hair regrowth. It is available in devices like laser combs, caps, or helmets.
Pros: Non-invasive and can be done at home with devices. Safe with minimal side effects. Can improve hair density and thickness over time.
Cons: Requires consistent use over several months for noticeable results. Results can vary between patients. Devices can be expensive, and insurance may not cover them.
4. Oral Medications:
Medications like spironolactone or finasteride are used to block the hormones responsible for hair thinning, particularly in women with hormonal imbalances such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or androgenetic alopecia.
Pros: Can effectively reduce hair thinning by addressing hormonal imbalances. Convenient as they are taken orally.
Cons: Potential side effects like weight gain, dizziness, or mood changes. Not suitable for all female patients, especially those of childbearing age (e.g., finasteride is not recommended during pregnancy).
5. Nutritional Supplements:
Supplements like biotin, iron, zinc, and vitamin D can support hair health and prevent hair loss caused by deficiencies in these nutrients.
Pros: Non-invasive and generally safe to use. Can address underlying deficiencies contributing to hair loss. Easy to incorporate into your daily routine.
Cons: Effectiveness depends on the presence of nutritional deficiencies. Overusing some supplements can cause adverse effects (e.g., too much iron can be harmful).
6. Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP):
SMP involves applying pigment to the scalp to create the illusion of fuller hair. This cosmetic treatment is ideal for women who want to improve the appearance of thinning areas without surgery.
Pros: Non-invasive with immediate results. Low maintenance once applied. Can provide a realistic look for patients with diffuse thinning.
Cons: Does not promote hair growth, just improves the appearance. Requires periodic touch-ups as the pigment may fade over time. Can be costly depending on the area treated.
7. Corticosteroids:
Corticosteroids reduce inflammation and suppress immune system activity, making them effective for treating hair loss caused by autoimmune or inflammatory conditions, such as alopecia areata or frontal fibrosing alopecia.
Pros: Reduces inflammation and promotes hair regrowth in cases of autoimmune-related hair loss. Offers multiple administration methods (topical, injectable, or oral) based on individual needs.
Cons: Possible side effects, including skin thinning (topical) or systemic effects like weight gain and high blood pressure (oral/injectable). Ineffective for non-inflammatory types of hair loss, such as androgenetic alopecia.
Hair Transplants For Women
Hair transplants can be an effective solution for women suffering from significant shedding or hair loss, especially in cases of female pattern baldness, hormonal changes, or scarring alopecia.
Female hair transplant procedures require a specialized approach, as women typically experience diffuse thinning rather than complete baldness. In most cases, only the donor area at the back or sides of the head is shaved, leaving the rest of the hair to cover the area during recovery. This is particularly important for female patients who may feel self-conscious about a shaved scalp.
Another crucial aspect of the procedure is the design of the hairline, which must reflect the natural, softer, and more rounded shape typical of female hairlines, unlike male hairlines, which often have sharper angles or recede, a feminine hairline features gentle curves and smooth transitions.

Choosing The Right Hair Loss Treatment For You
At Civas&Akpınar Hair Transplant Clinic in Turkey, we have extensive experience working with female patients, offering tailored solutions for conditions like female pattern baldness and diffuse thinning.
Our team of expert dermatologists carefully assesses each patient’s scalp health and hair characteristics to recommend the most suitable treatment. Whether it’s non-surgical options or surgical solutions such as Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) hair transplant, we ensure a customized approach that meets the needs of each patient.
With a focus on delivering natural-looking, long-lasting results, we help women restore not just their hair but also their confidence.
To learn more about the best hair loss treatment options for you, please fill out our contact form, and our team will guide you through the next steps.

