FUE vs FUT Hair Transplant: What’s the Best Method?
FUE and FUT are the main methods used to collect follicles from the donor area. FUE involves removing the grafts one by one from the donor area using special instruments. FUT involves cutting grafts from a strip of scalp obtained from the back or sides of the head.
In both procedures, traces of hair transplantation are visible only for a week. Patients can return to normal daily activities the second day after the procedure, and new hair growth begins within 2 to 3 months and is usually complete within 10 to 12 months.
Keep in mind that surgeons who are not fully qualified in both techniques will likely only suggest one technique. It is better to choose a doctor who can perform both techniques at an expert level. With a well-trained hair transplant staff and hair transplant surgeon, rapid healing, minimal trauma, natural angles, direction and distribution of grafts can be easily achieved in both FUE and FUT.
Dr. Civas, an ABHRS (American Board of Hair Restoration) Certified Surgeon, has the artistic skill and expert skills that always provide natural-looking results with both FUE and FUT.
Understanding Hair Transplantation Techniques
Hair transplantation techniques have evolved significantly over the years, offering patients suffering from hair loss effective solutions to restore their natural hairline and density. These techniques primarily include Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT).
FUE involves the extraction of individual hair follicles from the donor area, typically the back or sides of the scalp, using a small punch tool.
On the other hand, FUT involves removing a strip of tissue from the donor area and dissecting it into individual grafts.
Both techniques aim to implant healthy hair follicles into the recipient area, where hair loss has occurred, to achieve natural-looking results. Understanding the nuances of these techniques is crucial for patients considering hair transplantation, as it allows them to make informed decisions regarding their treatment options and expected outcomes.
The Basics: FUT And FUE Hair Transplant Explained
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) are two primary methods used in hair transplantation, each with its own unique approach. Both techniques aim to harvest healthy hair follicles for transplantation into the recipient area, where hair loss has occurred, to achieve natural-looking results. Understanding the fundamental differences between FUT and FUE is essential for patients considering hair transplantation, as it allows them to choose the method best suited to their needs and preferences.
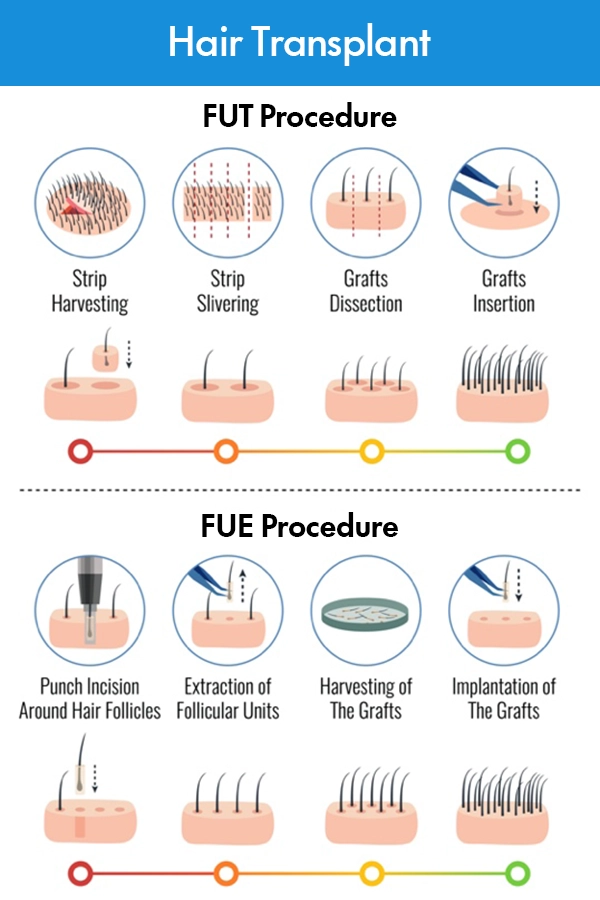

Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT):
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), also known as strip harvesting, is a traditional hair transplantation technique that involves the removal of a narrow strip of tissue from the donor area.
This strip is typically taken from the back or sides of the scalp, where hair is abundant and less susceptible to hair loss. After the strip is carefully removed, the hair transplant surgeon sutures the donor area, leaving a linear scar that can be concealed by surrounding hair. The strip of tissue is then dissected under a microscope into individual follicular units, which are subsequently transplanted into the recipient area.
While FUT may result in a more noticeable scar compared to FUE, it can be a suitable option for patients who require a larger number of grafts. Additionally, FUT allows for the preservation of the surrounding tissue, which can enhance graft survival and yield natural-looking results, particularly in cases of advanced hair loss.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE):
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is a sophisticated hair transplantation technique known for its minimally invasive nature and precise extraction process.
During FUE, individual follicular units, comprising one to four hairs, are meticulously harvested directly from the donor area using a specialized punch tool. The diameter of these punches typically ranges from 0.6mm to 1.0mm, allowing for precise extraction while minimizing trauma to the surrounding tissues. The donor hairs are usually extracted from the back or sides of the scalp, where hair is genetically programmed to be more resistant to balding.
FUE does not involve the removal of a strip of scalp tissue, which results in less discomfort and a quicker recovery time compared to other methods. Additionally, FUE leaves behind tiny, circular scars at the extraction sites, which are less noticeable and more dispersed, making it an ideal choice for patients who prefer to wear shorter hairstyles. or prefer a more cost-effective procedure.
Comparing FUT vs FUE Hair Transplant
The choice between Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is a crucial decision for those seeking to address hair loss concerns. Both techniques offer unique advantages and drawbacks, necessitating a thorough examination to determine the most suitable approach. This comparison table provides a comprehensive overview of the key differences between Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE),shedding light on their respective benefits and limitations to guide patients towards informed decisions regarding their hair restoration journey.
FUE vs FUT Hair Transplant
| Hair Transplant Technique | Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) | Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) |
|---|---|---|
| Donor Area Harvesting | Involves the removal of a strip of tissue from the donor area. | Involves the extraction of individual follicular units directly from the donor area. |
| Scarring | Leaves a linear scar at the donor site, which may be noticeable and require longer hair to conceal. | Leaves tiny, circular scars at the extraction sites, which are less noticeable and easier to conceal, allowing for shorter hairstyles. |
| Recovery Time | Typically involves a longer recovery time due to the need for sutures and the healing of the linear scar. | Generally involves a shorter recovery time as it does not require sutures and results in minimal trauma to the scalp. |
| Graft Yield | Allows for the extraction of a larger number of grafts in a single session, making it suitable for individuals requiring a higher hair density. | May result in fewer grafts per session compared to FUT, particularly in cases where a large number of grafts are required. |
| Cost | Can be more cost-effective for harvesting a large number of grafts in a single session. | Generally more expensive due to the labor-intensive nature of the procedure and advanced technology required for harvesting individual follicular units. |
| Ideal Candidates | Suitable for patients with advanced hair loss or those requiring a significant number of grafts. | Ideal for patients who prefer shorter hairstyles or want to avoid visible scarring, as well as those with limited donor hair or extensive scarring from previous surgeries. |
| Risk of Transection | Minimal risk of transection, as grafts are harvested under direct visualization. | Carries a risk of transection, especially in inexperienced hands or when extracting grafts from fine or curly hair, which can affect graft survival rates. |
| Flexibility in Styling | May restrict hairstyle options due to the presence of a linear scar at the donor site. | Offers greater flexibility in hairstyles without restriction, as there is no linear scar at the donor site. |
Hair Transplant Procedure: FUT vs FUE Step-by-Step
The procedure for Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) involve meticulous steps tailored to each technique, ensuring optimal results for hair restoration.
FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation):
- Donor Strip Excision: The surgical process begins with the marking and numbing of the donor area, followed by the removal of a narrow strip of tissue from the scalp. This strip is typically harvested from the back or sides of the head, where hair is abundant.
- Strip Dissection: The excised donor strip is carefully dissected under a microscope by trained technicians to separate individual follicular units from the surrounding tissue.
- Graft Preparation: Once dissected, the individual follicular units are meticulously prepared for transplantation, ensuring the viability and integrity of each graft.
- Recipient Area Preparation: The recipient area is prepared by creating tiny incisions or recipient sites according to the patient’s natural hairline and desired hair density.
- Graft Implantation: The prepared follicular units are delicately implanted into the recipient sites, following the predetermined pattern to achieve optimal aesthetic results
- Closure of Donor Area: Following graft harvesting, the donor area is sutured or closed using advanced techniques to minimize scarring and promote optimal healing.
- Post-Operative Care: Patients are provided with comprehensive post-operative instructions, including medication, wound care, and follow-up appointments to monitor progress and address any concerns.
FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction):
- Donor Area Preparation: The procedure commences with the marking of the donor area, typically located at the back or sides of the scalp. This area is chosen for its stable hair growth and resistance to balding.
- Anesthesia Administration: Local anesthesia is administered to numb the donor area, ensuring minimal discomfort for the patient during the extraction process.
- Individual Graft Extraction: Using a specialized punch tool with a diameter ranging from 0.6mm to 1.0mm, the surgeon extracts individual follicular units one at a time. This precise extraction method minimizes trauma to the surrounding tissues.
- Graft Harvesting: Each extracted graft is carefully inspected and prepared for transplantation. The harvested follicular units typically consist of one to four hairs.
- Recipient Area Preparation: Meanwhile, the recipient area, where hair loss has occurred, is prepared for graft implantation. Tiny incisions or recipient sites are made according to the natural hairline and desired density.
- Graft Implantation: The harvested follicular units are meticulously transplanted into the recipient sites, ensuring proper angulation and orientation to achieve a natural appearance.
- Post-Operative Care: Following the procedure, patients are provided with detailed instructions for post-operative care, including medication, cleaning protocols, and follow-up appointments to monitor progress.
Recovery and Healing: What to Expect After FUT and FUE Hair Transplant?
For patients undergoing Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) hair transplant, the recovery and healing process typically spans several weeks to months. Initially, patients may experience mild discomfort, swelling, and tightness around the donor area, which usually subside within a week or two. Full recovery from the FUT hair transplant procedure, including the healing of the donor scar, may take several weeks to months, depending on the patient’s healing abilities and adherence to post-operative care instructions. Over the following weeks, the transplanted follicles enter a dormant phase before gradually shedding, making way for new hair growth. Patients can expect to see noticeable improvement in hair density within three to four months post-surgery, with final results becoming apparent after about a year.
On the other hand, Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) offers a shorter recovery period compared to FUT due to its minimally invasive nature. Following the hair transplant procedure, patients may experience minor swelling and redness in the donor and recipient areas, which typically resolve within a few days. Since FUE hair transplant does not involve a linear incision like FUT, there is minimal scarring, allowing for quicker healing and less post-operative discomfort. Most patients can return to their normal activities within a week, although strenuous exercise should be avoided for a few weeks to promote optimal healing. Similar to FUT, the transplanted follicles undergo a temporary shedding phase before regrowing hair within a few months, leading to significant improvement in hair density and appearance. Overall, the recovery time for FUE is generally shorter compared to FUT, making it an attractive option for those seeking minimal downtime.
Cost Considerations: FUT vs FUE Hair Transplant
When considering hair transplant options, understanding the cost differences between Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) is crucial. FUT hair transplant typically involves a lower cost per graft compared to FUE, primarily because it is a more streamlined procedure that allows for the transplantation of a larger number of grafts in a single session. On the other hand, FUE hair transplant tends to be more labor-intensive and time-consuming, leading to a higher cost per graft. Additionally, factors such as the expertise of the surgeon, the clinic’s location, and the extent of hair loss can influence overall price of hair transplant procedures. While FUT may initially seem more affordable, it’s essential to consider long-term factors such as scarring and downtime, which could impact lifestyle and future expenses. Ultimately, patients should weigh the financial aspects alongside the benefits and drawbacks of each technique to make an informed decision that aligns with their goals and budget.
Results And Success Rates: Which Is Better FUT Or FUE Hair Transplant?
When comparing the results and success rates of Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) hair transplant procedures, several factors come into play. Both techniques can achieve natural-looking results when performed by experienced surgeons, but the suitability of each method depends on individual factors such as hair type, extent of hair loss, and donor hair availability.
FUT hair transplant often yields higher graft survival rates due to the shorter time grafts spend outside the body during transplantation. It is particularly advantageous for patients requiring a large number of grafts.
On the other hand, FUE hair transplant offers the benefit of minimal scarring and a quicker recovery time, making it preferable for patients concerned about visible scars or those with a preference for shorter downtime.
Success rates for both procedures are generally high when performed by skilled practitioners in reputable clinics. Ultimately, the choice between FUT and FUE should be based on a comprehensive consultation with a qualified hair transplant specialist who can assess the needs and goals of the patient to determine the most suitable approach for achieving desired results.
Risks And Complications Of FUT And FUE Hair Transplant
When considering Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) hair transplant procedures, it’s essential to be aware of potential risks and complications. One primary concern is the linear scar that results from the strip of scalp tissue being removed from the donor area. While skilled hair transplant surgeons aim to minimize scarring, some patients may experience widened scars or keloid formation, particularly those with a predisposition to scarring. Additionally, there is a risk of nerve damage, which can lead to temporary or permanent numbness in the scalp. Infection and bleeding are also potential complications, although rare when proper surgical techniques and post-operative care are followed diligently. Another consideration is the possibility of “shock loss,” where existing hair in the donor area or adjacent regions may temporarily shed following surgery before regrowth occurs.
Similarly, Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) hair transplant procedures carry their own set of risks and complications. While FUE minimizes the risk of a linear scar, it is not without potential drawbacks. One common issue is follicular transection, where grafts are inadvertently damaged during extraction, leading to reduced graft survival and compromised results. Additionally, patients may experience temporary swelling, redness, and discomfort in the donor and recipient areas following surgery, although these symptoms typically subside within a few days to weeks. In rare cases, patients may develop post-operative infections or cysts around transplanted follicles, necessitating medical intervention.
Scarring: FUT vs FUE Hair Transplant
When comparing scarring between Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) hair transplant procedures, significant differences exist. FUT hair transplant typically results in a linear scar along the donor area where the strip of scalp tissue is removed, which may be noticeable, particularly with shorter haircuts. In contrast, FUE hair transplant leaves tiny, dot-like scars scattered throughout the donor region, making them less conspicuous and easier to conceal, even with shorter hairstyles. However, patients with a predisposition to keloid scarring or those with limited donor hair may still experience challenges with FUE scarring.
Factors To Consider Before Choosing FUT Or FUE Hair Transplant Technique
Before opting for a hair transplant procedure, it’s essential to consider various factors to determine which technique—Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) or Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE)—best aligns with your needs and preferences.
- Scarring Concerns: Evaluate your tolerance for visible scarring. FUT typically leaves a linear scar, while FUE results in scattered dot-like scars.
- Hair Type and Density: Consider your hair type and density, as well as the extent of hair loss. FUT may be more suitable for patients requiring a large number of grafts, whereas FUE is ideal for those with limited donor hair or a preference for minimal scarring.
- Recovery Time: Assess your availability for downtime and recovery. FUT generally has a longer recovery period due to the strip harvesting technique, whereas FUE involves minimal downtime.
- Cost Considerations: Determine your budget and financial considerations. FUT often has a lower cost per graft compared to FUE, but long-term factors such as scarring should also be taken into account.
- Success Rates: Research the success rates of both techniques and consult with qualified surgeons to understand the potential outcomes based on your specific case.
- Risks and Complications: Understand the potential risks and complications associated with each technique, such as scarring, infection, follicular transection, and nerve damage, and weigh them against the benefits.
- Expertise of Surgeon: Choose a reputable and experienced surgeon who specializes in the chosen technique to ensure optimal results and minimize risks.
- Personal Preferences: Consider your personal preferences regarding scarring, recovery time, and overall aesthetic goals when making your decision.
Expert Insights: Perspectives of Surgeons from Civas Hair Transplant Turkey on FUT and FUE Hair Transplant
At Civas Hair Transplant, one of the best hair transplant clinics in Turkey, our world class surgeons, Dr. Ekrem Civas and Dr. Ümit Akpınar emphasize the significance of recognizing that each case of hair loss is unique, and therefore, requires an individualized treatment approach tailored to the patient’s specific needs. They underscore the importance of consulting with a dermatologist specialized in hair loss treatments to thoroughly assess the underlying causes of hair loss before determining an appropriate treatment plan.
By understanding the root cause of hair loss, patients and surgeons can collaborate to devise a customized strategy that addresses their concerns effectively. This personalized approach extends to the selection of hair transplant techniques, where the expertise of the surgeon plays a crucial role in guiding patients towards the most suitable option—whether it be Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) or Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE). By fostering open communication and collaboration between patients and surgeons, Civas Hair Transplant Turkey aims to ensure that patients receive tailored solutions that align with their goals and yield optimal results in their hair restoration journey.
March 25, 2025


