What You Need to Know About Post-Hair Transplant Folliculitis
Folliculitis after hair transplant is a postoperative inflammatory condition in which the hair follicles become irritated or infected. Clinical studies report that it can be seen in approximately 10-12% of patients, making it one of the most frequent minor complications following hair transplantation.
In this blog, we will explain why post-hair transplant folliculitis develops, how to distinguish normal healing from true infection, which risk factors increase its likelihood, and the most effective prevention methods.
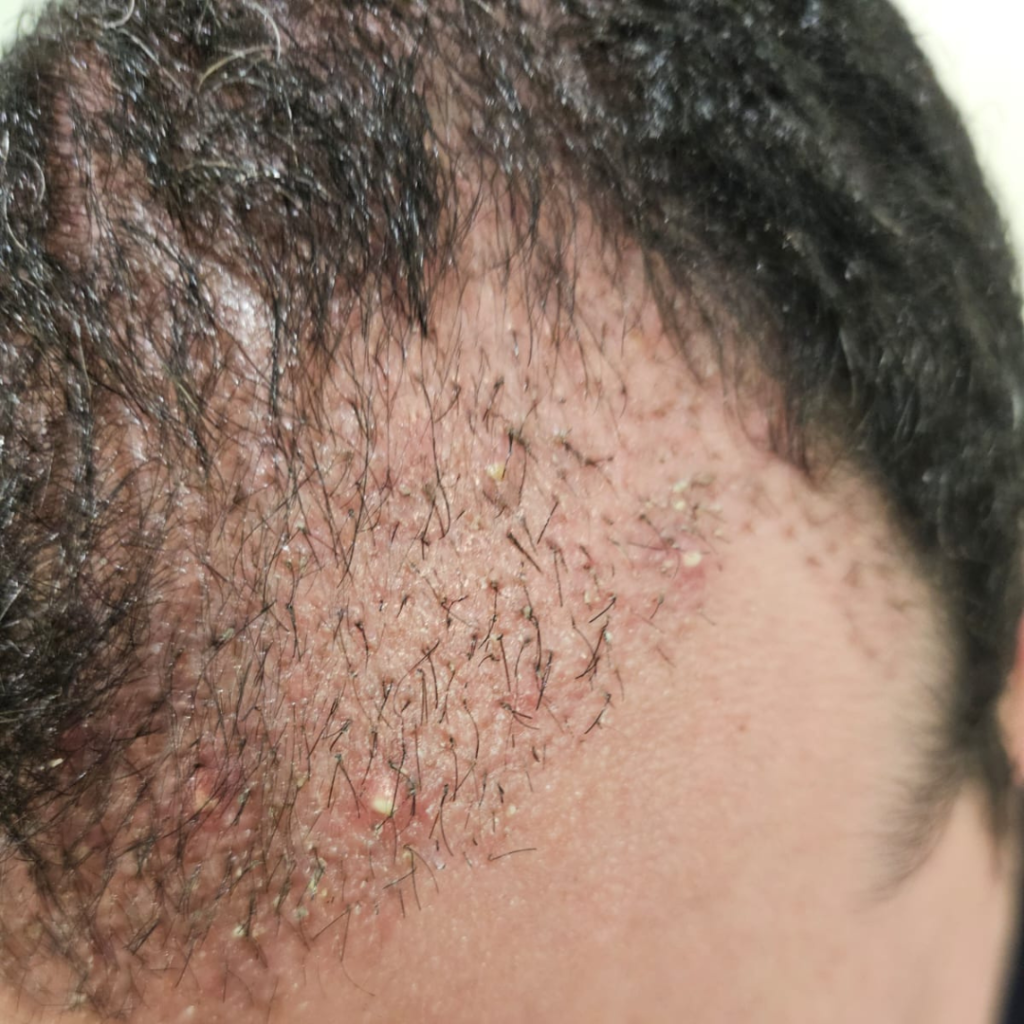

What is Folliculitis After Hair Transplant?
Folliculitis after hair transplant is an inflammatory or infectious reaction of the hair follicles that appears as small red bumps or pus-filled pimples around transplanted or donor hairs, usually caused by blocked follicles, bacteria, surgical trauma, or ingrown hairs during healing.
This condition can develop in both the recipient and donor areas, appearing around transplanted or extracted follicular units and is more pronounced than the normal postoperative healing response.
Is Post-Hair Transplant Folliculitis Common?
Yes, folliculitis after hair transplant is relatively common, especially in the early postoperative period. Clinical research shows that approximately 12.11% of patients develop folliculitis after a hair restoration procedure. This means that around 1 in every 8-9 patients may experience temporary scalp inflammation, redness, or pimples during healing.
However, true pathological inflammatory complications from Folliculitis are rare. Clinical research reports an incidence of only about 0.08%, and among these uncommon cases, most were:
- Lichen planopilaris: 7 cases
- Erosive pustular dermatosis: 2 cases
- Superficial folliculitis: 1 case
What Does Folliculitis Look Like After Your Hair Transplant?
The symptoms of folliculitis after a hair transplant may vary in severity, but it typically presents with the following clinical signs:
- Small red bumps or raised papules around transplanted or extracted follicles
- White-tipped pimples after hair transplant filled with pus (pustules)
- Tenderness or a burning sensation in the affected area
- Itching or mild pain in inflamed follicles
- In some cases, yellowish discharge indicating possible infection
- Occasionally deeper, more painful nodules suggesting deeper inflammation after hair transplant
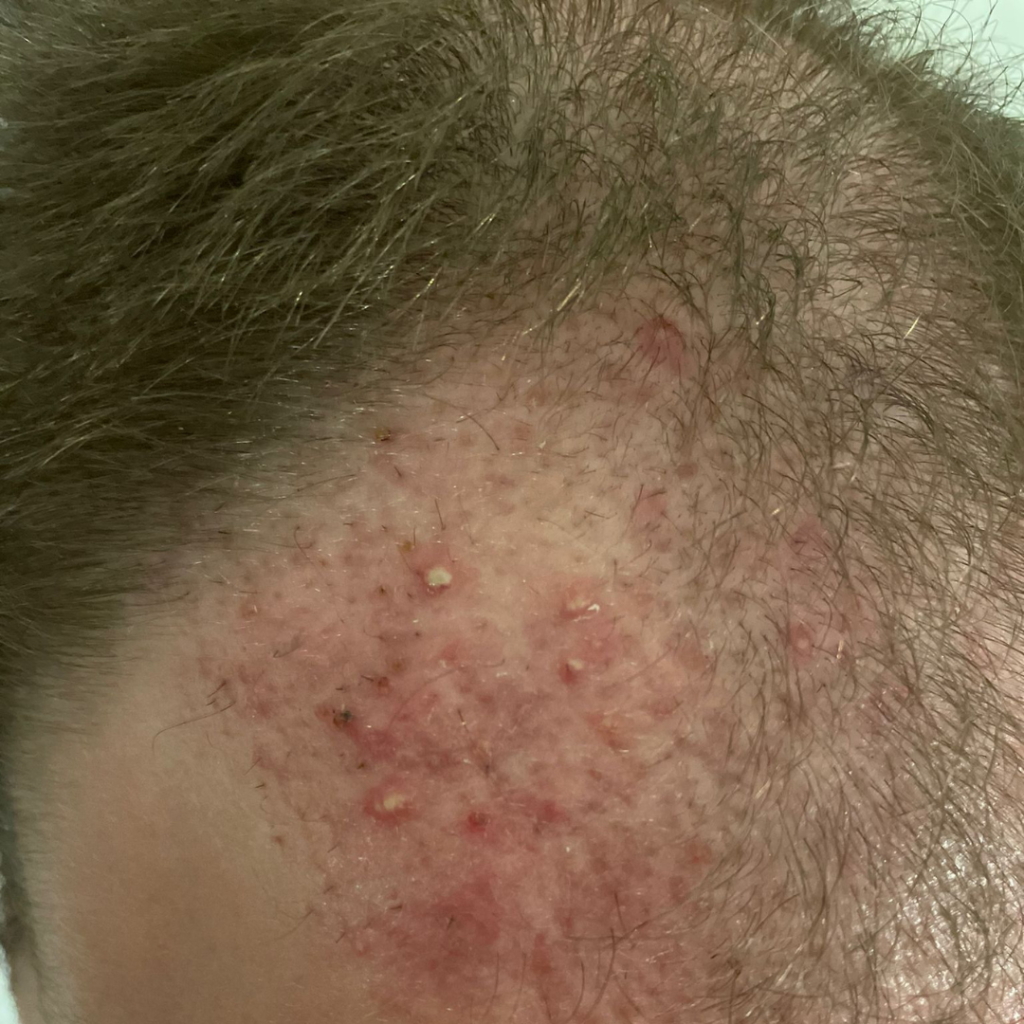

Difference Between Normal Healing and Folliculitis
After hair transplantation, mild redness, small scabs, and slight swelling around the grafts are part of the normal healing process and usually improve steadily without pain or pus formation.
In contrast, folliculitis presents as inflamed, tender bumps or pimples that may contain pus and are often surrounded by more intense, localized redness. Unlike normal healing, these lesions may increase in number, become painful or itchy, and in some cases show signs of infection, such as warmth or discharge.
Types of Folliculitis After Hair Transplant
Sterile (Inflammatory) Folliculitis
Sterile Folliculitis is caused by a non-infectious inflammatory response of the immune system to:
- Surgical trauma
- Sebum leakage
- Graft manipulation
Although it may resemble pimples after hair transplant, it is not a true infection and usually resolves with anti-inflammatory care rather than antibiotics.
Bacterial Folliculitis (Infected Hair Grafts)
Bacterial folliculitis after hair transplant develops when microorganisms, most commonly staphylococci, colonize the healing follicles, leading to true folliculitis with active infection. It may arise from:
- Pre-existing bacterial colonization of the scalp
- Inadequate hygiene
- Contamination through contact
It is more frequently seen in patients with immune-related conditions such as diabetes mellitus or those using immunosuppressive medications.
Depending on the extent of inflammation and the characteristics of the discharge, culture and antibiogram testing are recommended so that antibiotic treatment can be tailored accordingly.
Foreign Body Reaction to Grafts
In some patients, the immune system reacts to:
- Hair fragments
- Crusts
- Lipid material released from damaged sebaceous glands.
This sterile reaction causes localized inflammation, forming firm red papules or pustules around the grafts. Although it mimics pimples, cultures are typically negative.
Traumatic Folliculitis After FUE and DHI
Mechanical irritation during extraction or implantation, such as friction, pressure, or micro-injury to surrounding tissue, can trigger follicular inflammation. Disruption of sebaceous glands during FUE or DHI may release fatty material into the dermis, provoking an immune response and resulting in localized redness, bumps, and inflammatory lesions typical of hair transplant and folliculitis related to surgical trauma.
Risk Factors Leading to Folliculitis After Hair Transplant
Dense Packing and High Graft Numbers
Transplanting more than 4,000 grafts or using very dense packing (>45 grafts/cm²) increases tissue trauma and can compromise local blood flow. Closely placed follicles are more susceptible to irritation, reduced oxygenation, and bacterial overgrowth, which can promote postoperative inflammation and pimple formation.
Summer Surgery and Excessive Sweating
Procedures performed during hot weather are associated with higher rates of hair transplant and folliculitis due to increased sweating, humidity, and sebum production. Moist environments facilitate bacterial proliferation and can aggravate redness, bumps, and inflammatory reactions around healing follicles.
Delayed Postoperative Care
Postponed or inadequate scalp cleansing allows crusts, debris, and microorganisms to accumulate around healing follicles, increasing the likelihood of inflammatory or infectious complications.
Diabetes and Weakened Immune System
Hair transplant patients with diabetes mellitus or those using immunosuppressive medications have impaired wound healing and reduced defense against microorganisms. As a result, they are at higher risk for developing bacterial post-hair transplant folliculitis, with a greater tendency for pustules, persistent redness, and delayed resolution.
When Does Folliculitis Appear After Hair Transplant?
Folliculitis can develop at different stages of the healing process, depending on the underlying cause and individual healing response.
Early-Onset Folliculitis (First Days)
Early-onset folliculitis usually appears within the first 3-7 days. It is often related to bacterial contamination, excessive sweating, occlusive dressings, or inadequate scalp hygiene.
Late-Onset Folliculitis (Weeks to Months Later)
Late-onset folliculitis typically develops several weeks to a few months after the procedure, often during the phase when transplanted hairs begin to regrow. It may be associated with ingrown hairs, keratin plugging, foreign body reactions, or residual low-grade infection. Lesions are usually localized, less painful, and may recur intermittently until the follicle fully stabilizes.
Does Folliculitis Affect Graft Survival?
In most cases, mild and promptly treated folliculitis does not have a significant impact on graft survival. Superficial inflammation limited to the upper part of the follicle usually resolves without damaging the transplanted hair roots.
However, when the condition becomes severe, persistent, or is caused by a true bacterial infection, the inflammatory process can extend deeper and compromise the follicular unit.
Prolonged swelling, pressure from pustules, and tissue ischemia may interfere with blood supply to the grafts, increasing the risk of poor growth or, in rare cases, permanent follicular damage.
How to Prevent Pimples After Hair Transplant?
Importance of Choosing The Right Surgeon
The skill and experience of the surgeon are crucial in preventing postoperative complications such as folliculitis. When surgery is performed under sterile conditions by a well-trained doctor, the risk of infection, excessive inflammation, and pimple formation in both the recipient and donor areas is significantly reduced.
Proper Scalp Hygiene and Washing Protocol
Gentle but regular cleansing helps remove dried blood, sebum, and bacteria that can block follicular openings. Using the clinic-recommended shampoo and washing technique reduces the risk of clogged pores and secondary infection while supporting healthy healing of both the recipient and donor areas.
Avoiding Mechanical Trauma and Scratching
Rubbing, scratching, tight headwear, or sleeping positions that cause friction can traumatize newly implanted follicles. Mechanical irritation may trigger inflammation, disrupt the follicular opening, and promote the formation of painful pimples or pustules.
Role of Prophylactic Antibiotics
In selected patients, such as those undergoing dense packing, large sessions, or with medical risk factors, short-term prophylactic antibiotics may be prescribed to reduce bacterial load during the early healing phase.
Importance of Dermatologic Evaluation
Early assessment by a dermatologist or the transplant surgeon is essential when redness, swelling, or pustules appear. Distinguishing between normal postoperative reactions and true folliculitis allows timely treatment, prevents progression, and protects the long-term survival of the transplanted grafts.
How To Treat Folliculitis After Hair Transplant?
Treatment of Sterile (Allergic) Folliculitis
Treatment focuses on reducing inflammation rather than using antibiotics. Topical corticosteroid lotions, soothing antiseptic washes, and avoiding friction or scratching are usually sufficient. These lesions often resolve on their own once the inflammatory response settles.
Treatment of Bacterial Folliculitis
When true infection is present, therapy should target the responsible microorganisms. Management may include topical or oral antibiotics effective against staphylococci, depending on severity. Good scalp hygiene and temporary modification of washing routines are also important. Prompt treatment prevents spread, abscess formation, and potential harm to healing grafts.
Over-the-Counter Treatments for Mild Folliculitis
Mild cases may improve with antiseptic shampoos, gentle cleansing solutions, and non-comedogenic topical products that reduce bacterial load and calm the skin. These options can support healing, but persistent or worsening symptoms should always be evaluated by a dermatologist.
When Culture and Antibiogram Are Needed
If pustules are widespread, recurrent, painful, or not responding to initial treatment, a bacterial culture and antibiogram should be performed. Identifying the exact pathogen and its antibiotic sensitivity allows targeted therapy and avoids unnecessary or ineffective antibiotic use.
Clinical Perspective from Dermatologists at Civas&Akpınar on Post-Transplant Folliculitis
According to the dermatologists at Civas&Akpınar Hair Transplant Clinic, most cases of postoperative folliculitis are mild, temporary, and manageable when recognized early. They stress that patients should seek medical evaluation if inflammation does not follow the normal pattern of healing or shows signs of progression.
Red Flags Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
- Rapidly spreading redness or swelling in the recipient or donor area
- Increasing pain or tenderness instead of gradual improvement
- Pus-filled lesions, especially with thick or foul-smelling discharge
- Fever or general malaise
- Deep, firm, or enlarging nodules suggestive of abscess formation
- Skin breakdown, ulceration, or early scarring changes
- Lack of response or worsening despite initial care
If you have concerns about your healing process, schedule a follow-up consultation with our specialists at Civas&Akpınar for a personal assessment.
FAQs: Hair Transplant And Folliculitis
Q: Why Do Pimples Occur After Hair Transplant?
A: They usually develop due to inflammation, blocked follicles, trapped hairs, or bacterial overgrowth during the healing process.
Q: Is it Safe to Pop Pimples After Hair Transplant?
A: No, squeezing pimples can introduce infection and damage healing grafts, so it should be avoided.
Q: What Are the Symptoms of Folliculitis After a Hair Transplant?
A: Symptoms of folliculitis after hair transplant include: small red bumps around grafts, white-tipped pus-filled pimples, itching or burning sensation, localized pain or tenderness, yellow discharge in infected cases and deep painful nodules (rare).
Q: What Causes Folliculitis After a Hair Transplant?
A: It can result from surgical trauma, foreign body reactions, poor hygiene, sweating, or bacterial contamination.
Q: Can Folliculitis Damage My Transplanted Hair?
A: If severe or left untreated, it may compromise graft survival and rarely lead to scarring.
Q: How Long Does It Take for Folliculitis to Resolve?
A: Most mild cases improve within a few days to two weeks with proper care.
Q: Are There Natural Remedies for Treating Folliculitis?
A: Gentle cleansing, avoiding irritation, and keeping the scalp dry can help, but medical treatment may be needed for infection.
Q: How Can I Prevent Folliculitis After My Hair Transplant?
A: Following hair transplant aftercare instructions, washing instructions, avoiding scratching, and attending follow-up visits greatly reduces the risk.
Q: Can Folliculitis Occur Weeks or Months After Surgery?
A: Yes, late-onset folliculitis can appear due to ingrown hairs, delayed inflammation, or secondary infection.


